Note
Click here to download the full example code
Gromov-Wasserstein Barycenter example¶
This example is designed to show how to use the Gromov-Wasserstein distance computation in POT.
# Author: Erwan Vautier <erwan.vautier@gmail.com>
# Nicolas Courty <ncourty@irisa.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pylab as pl
from sklearn import manifold
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
import ot
Smacof MDS¶
This function allows to find an embedding of points given a dissimilarity matrix that will be given by the output of the algorithm
def smacof_mds(C, dim, max_iter=3000, eps=1e-9):
"""
Returns an interpolated point cloud following the dissimilarity matrix C
using SMACOF multidimensional scaling (MDS) in specific dimensionned
target space
Parameters
----------
C : ndarray, shape (ns, ns)
dissimilarity matrix
dim : int
dimension of the targeted space
max_iter : int
Maximum number of iterations of the SMACOF algorithm for a single run
eps : float
relative tolerance w.r.t stress to declare converge
Returns
-------
npos : ndarray, shape (R, dim)
Embedded coordinates of the interpolated point cloud (defined with
one isometry)
"""
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=3)
mds = manifold.MDS(
dim,
max_iter=max_iter,
eps=1e-9,
dissimilarity='precomputed',
n_init=1)
pos = mds.fit(C).embedding_
nmds = manifold.MDS(
2,
max_iter=max_iter,
eps=1e-9,
dissimilarity="precomputed",
random_state=rng,
n_init=1)
npos = nmds.fit_transform(C, init=pos)
return npos
Data preparation¶
The four distributions are constructed from 4 simple images
def im2mat(I):
"""Converts and image to matrix (one pixel per line)"""
return I.reshape((I.shape[0] * I.shape[1], I.shape[2]))
square = pl.imread('../data/square.png').astype(np.float64)[:, :, 2]
cross = pl.imread('../data/cross.png').astype(np.float64)[:, :, 2]
triangle = pl.imread('../data/triangle.png').astype(np.float64)[:, :, 2]
star = pl.imread('../data/star.png').astype(np.float64)[:, :, 2]
shapes = [square, cross, triangle, star]
S = 4
xs = [[] for i in range(S)]
for nb in range(4):
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if shapes[nb][i, j] < 0.95:
xs[nb].append([j, 8 - i])
xs = np.array([np.array(xs[0]), np.array(xs[1]),
np.array(xs[2]), np.array(xs[3])])
Barycenter computation¶
ns = [len(xs[s]) for s in range(S)]
n_samples = 30
"""Compute all distances matrices for the four shapes"""
Cs = [sp.spatial.distance.cdist(xs[s], xs[s]) for s in range(S)]
Cs = [cs / cs.max() for cs in Cs]
ps = [ot.unif(ns[s]) for s in range(S)]
p = ot.unif(n_samples)
lambdast = [[float(i) / 3, float(3 - i) / 3] for i in [1, 2]]
Ct01 = [0 for i in range(2)]
for i in range(2):
Ct01[i] = ot.gromov.gromov_barycenters(n_samples, [Cs[0], Cs[1]],
[ps[0], ps[1]
], p, lambdast[i], 'square_loss', # 5e-4,
max_iter=100, tol=1e-3)
Ct02 = [0 for i in range(2)]
for i in range(2):
Ct02[i] = ot.gromov.gromov_barycenters(n_samples, [Cs[0], Cs[2]],
[ps[0], ps[2]
], p, lambdast[i], 'square_loss', # 5e-4,
max_iter=100, tol=1e-3)
Ct13 = [0 for i in range(2)]
for i in range(2):
Ct13[i] = ot.gromov.gromov_barycenters(n_samples, [Cs[1], Cs[3]],
[ps[1], ps[3]
], p, lambdast[i], 'square_loss', # 5e-4,
max_iter=100, tol=1e-3)
Ct23 = [0 for i in range(2)]
for i in range(2):
Ct23[i] = ot.gromov.gromov_barycenters(n_samples, [Cs[2], Cs[3]],
[ps[2], ps[3]
], p, lambdast[i], 'square_loss', # 5e-4,
max_iter=100, tol=1e-3)
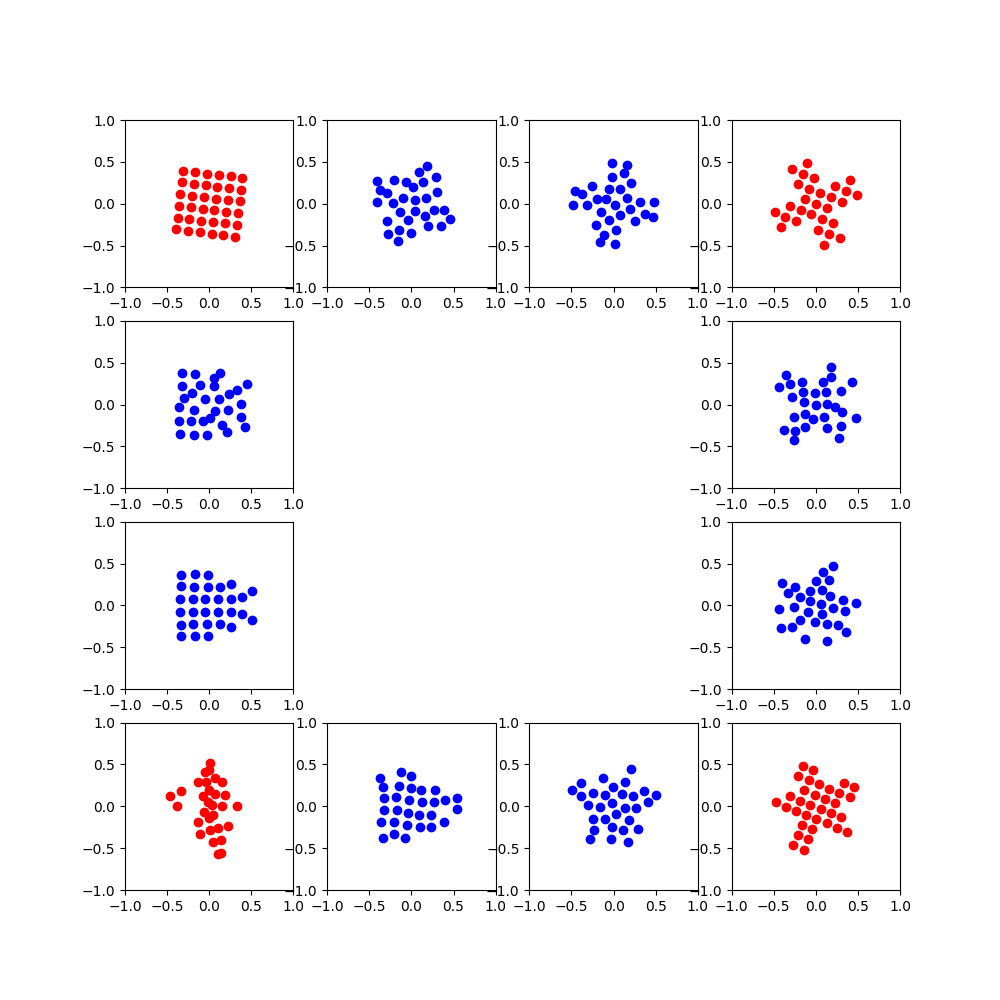
Visualization¶
The PCA helps in getting consistency between the rotations
clf = PCA(n_components=2)
npos = [0, 0, 0, 0]
npos = [smacof_mds(Cs[s], 2) for s in range(S)]
npost01 = [0, 0]
npost01 = [smacof_mds(Ct01[s], 2) for s in range(2)]
npost01 = [clf.fit_transform(npost01[s]) for s in range(2)]
npost02 = [0, 0]
npost02 = [smacof_mds(Ct02[s], 2) for s in range(2)]
npost02 = [clf.fit_transform(npost02[s]) for s in range(2)]
npost13 = [0, 0]
npost13 = [smacof_mds(Ct13[s], 2) for s in range(2)]
npost13 = [clf.fit_transform(npost13[s]) for s in range(2)]
npost23 = [0, 0]
npost23 = [smacof_mds(Ct23[s], 2) for s in range(2)]
npost23 = [clf.fit_transform(npost23[s]) for s in range(2)]
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax1 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (0, 0))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax1.scatter(npos[0][:, 0], npos[0][:, 1], color='r')
ax2 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (0, 1))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax2.scatter(npost01[1][:, 0], npost01[1][:, 1], color='b')
ax3 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (0, 2))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax3.scatter(npost01[0][:, 0], npost01[0][:, 1], color='b')
ax4 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (0, 3))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax4.scatter(npos[1][:, 0], npos[1][:, 1], color='r')
ax5 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (1, 0))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax5.scatter(npost02[1][:, 0], npost02[1][:, 1], color='b')
ax6 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (1, 3))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax6.scatter(npost13[1][:, 0], npost13[1][:, 1], color='b')
ax7 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (2, 0))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax7.scatter(npost02[0][:, 0], npost02[0][:, 1], color='b')
ax8 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (2, 3))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax8.scatter(npost13[0][:, 0], npost13[0][:, 1], color='b')
ax9 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (3, 0))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax9.scatter(npos[2][:, 0], npos[2][:, 1], color='r')
ax10 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (3, 1))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax10.scatter(npost23[1][:, 0], npost23[1][:, 1], color='b')
ax11 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (3, 2))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax11.scatter(npost23[0][:, 0], npost23[0][:, 1], color='b')
ax12 = pl.subplot2grid((4, 4), (3, 3))
pl.xlim((-1, 1))
pl.ylim((-1, 1))
ax12.scatter(npos[3][:, 0], npos[3][:, 1], color='r')
Out:
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x7f6078c55d90>
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.286 seconds)