Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Semi-relaxed (Fused) Gromov-Wasserstein example
This example is designed to show how to use the semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein and the semi-relaxed Fused Gromov-Wasserstein divergences.
sr(F)GW between two graphs G1 and G2 searches for a reweighing of the nodes of G2 at a minimal (F)GW distance from G1.
First, we generate two graphs following Stochastic Block Models, then show how to compute their srGW matchings and illustrate them. These graphs are then endowed with node features and we follow the same process with srFGW.
[48] Cédric Vincent-Cuaz, Rémi Flamary, Marco Corneli, Titouan Vayer, Nicolas Courty. “Semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein divergence and applications on graphs” International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2021.
# Author: Cédric Vincent-Cuaz <cedvincentcuaz@gmail.com>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as pl
from ot.gromov import (
semirelaxed_gromov_wasserstein,
semirelaxed_fused_gromov_wasserstein,
gromov_wasserstein,
fused_gromov_wasserstein,
)
import networkx
from networkx.generators.community import stochastic_block_model as sbm
Generate two graphs following Stochastic Block models of 2 and 3 clusters.
N2 = 20 # 2 communities
N3 = 30 # 3 communities
p2 = [[1.0, 0.1], [0.1, 0.9]]
p3 = [[1.0, 0.1, 0.0], [0.1, 0.95, 0.1], [0.0, 0.1, 0.9]]
G2 = sbm(seed=0, sizes=[N2 // 2, N2 // 2], p=p2)
G3 = sbm(seed=0, sizes=[N3 // 3, N3 // 3, N3 // 3], p=p3)
C2 = networkx.to_numpy_array(G2)
C3 = networkx.to_numpy_array(G3)
h2 = np.ones(C2.shape[0]) / C2.shape[0]
h3 = np.ones(C3.shape[0]) / C3.shape[0]
# Add weights on the edges for visualization later on
weight_intra_G2 = 5
weight_inter_G2 = 0.5
weight_intra_G3 = 1.0
weight_inter_G3 = 1.5
weightedG2 = networkx.Graph()
part_G2 = [G2.nodes[i]["block"] for i in range(N2)]
for node in G2.nodes():
weightedG2.add_node(node)
for i, j in G2.edges():
if part_G2[i] == part_G2[j]:
weightedG2.add_edge(i, j, weight=weight_intra_G2)
else:
weightedG2.add_edge(i, j, weight=weight_inter_G2)
weightedG3 = networkx.Graph()
part_G3 = [G3.nodes[i]["block"] for i in range(N3)]
for node in G3.nodes():
weightedG3.add_node(node)
for i, j in G3.edges():
if part_G3[i] == part_G3[j]:
weightedG3.add_edge(i, j, weight=weight_intra_G3)
else:
weightedG3.add_edge(i, j, weight=weight_inter_G3)
Compute their semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein divergences
# 0) GW(C2, h2, C3, h3) for reference
OT, log = gromov_wasserstein(C2, C3, h2, h3, symmetric=True, log=True)
gw = log["gw_dist"]
# 1) srGW(C2, h2, C3)
OT_23, log_23 = semirelaxed_gromov_wasserstein(
C2, C3, h2, symmetric=True, log=True, G0=None
)
srgw_23 = log_23["srgw_dist"]
# 2) srGW(C3, h3, C2)
OT_32, log_32 = semirelaxed_gromov_wasserstein(
C3, C2, h3, symmetric=None, log=True, G0=OT.T
)
srgw_32 = log_32["srgw_dist"]
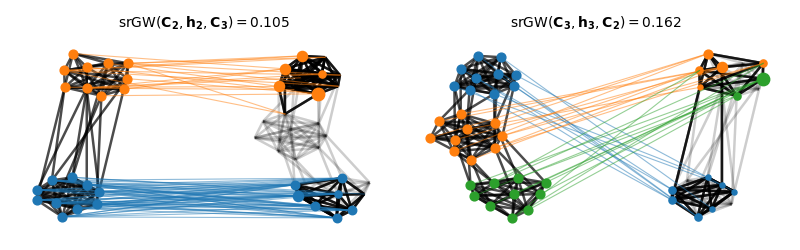
print("GW(C2, C3) = ", gw)
print("srGW(C2, h2, C3) = ", srgw_23)
print("srGW(C3, h3, C2) = ", srgw_32)
GW(C2, C3) = 0.24722222222222215
srGW(C2, h2, C3) = 0.07000000000000006
srGW(C3, h3, C2) = 0.17111111111111116
Visualization of the semi-relaxed Gromov-Wasserstein matchings
We color nodes of the graph on the right - then project its node colors based on the optimal transport plan from the srGW matching
def draw_graph(
G,
C,
nodes_color_part,
Gweights=None,
pos=None,
edge_color="black",
node_size=None,
shiftx=0,
seed=0,
):
if pos is None:
pos = networkx.spring_layout(G, scale=1.0, seed=seed)
if shiftx != 0:
for k, v in pos.items():
v[0] = v[0] + shiftx
alpha_edge = 0.7
width_edge = 1.8
if Gweights is None:
networkx.draw_networkx_edges(
G, pos, width=width_edge, alpha=alpha_edge, edge_color=edge_color
)
else:
# We make more visible connections between activated nodes
n = len(Gweights)
edgelist_activated = []
edgelist_deactivated = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if Gweights[i] * Gweights[j] * C[i, j] > 0:
edgelist_activated.append((i, j))
elif C[i, j] > 0:
edgelist_deactivated.append((i, j))
networkx.draw_networkx_edges(
G,
pos,
edgelist=edgelist_activated,
width=width_edge,
alpha=alpha_edge,
edge_color=edge_color,
)
networkx.draw_networkx_edges(
G,
pos,
edgelist=edgelist_deactivated,
width=width_edge,
alpha=0.1,
edge_color=edge_color,
)
if Gweights is None:
for node, node_color in enumerate(nodes_color_part):
networkx.draw_networkx_nodes(
G,
pos,
nodelist=[node],
node_size=node_size,
alpha=1,
node_color=node_color,
)
else:
scaled_Gweights = Gweights / (0.5 * Gweights.max())
nodes_size = node_size * scaled_Gweights
for node, node_color in enumerate(nodes_color_part):
networkx.draw_networkx_nodes(
G,
pos,
nodelist=[node],
node_size=nodes_size[node],
alpha=1,
node_color=node_color,
)
return pos
def draw_transp_colored_srGW(
G1,
C1,
G2,
C2,
part_G1,
p1,
p2,
T,
pos1=None,
pos2=None,
shiftx=4,
switchx=False,
node_size=70,
seed_G1=0,
seed_G2=0,
):
starting_color = 0
# get graphs partition and their coloring
part1 = part_G1.copy()
unique_colors = ["C%s" % (starting_color + i) for i in np.unique(part1)]
nodes_color_part1 = []
for cluster in part1:
nodes_color_part1.append(unique_colors[cluster])
nodes_color_part2 = []
# T: getting colors assignment from argmin of columns
for i in range(len(G2.nodes())):
j = np.argmax(T[:, i])
nodes_color_part2.append(nodes_color_part1[j])
pos1 = draw_graph(
G1,
C1,
nodes_color_part1,
Gweights=p1,
pos=pos1,
node_size=node_size,
shiftx=0,
seed=seed_G1,
)
pos2 = draw_graph(
G2,
C2,
nodes_color_part2,
Gweights=p2,
pos=pos2,
node_size=node_size,
shiftx=shiftx,
seed=seed_G2,
)
for k1, v1 in pos1.items():
for k2, v2 in pos2.items():
if T[k1, k2] > 0:
pl.plot(
[pos1[k1][0], pos2[k2][0]],
[pos1[k1][1], pos2[k2][1]],
"-",
lw=0.8,
alpha=0.5,
color=nodes_color_part1[k1],
)
return pos1, pos2
node_size = 40
fontsize = 10
seed_G2 = 0
seed_G3 = 4
pl.figure(1, figsize=(8, 2.5))
pl.clf()
pl.subplot(121)
pl.axis("off")
pl.axis
pl.title(
r"srGW$(\mathbf{C_2},\mathbf{h_2},\mathbf{C_3}) =%s$" % (np.round(srgw_23, 3)),
fontsize=fontsize,
)
hbar2 = OT_23.sum(axis=0)
pos1, pos2 = draw_transp_colored_srGW(
weightedG2,
C2,
weightedG3,
C3,
part_G2,
p1=None,
p2=hbar2,
T=OT_23,
shiftx=1.5,
node_size=node_size,
seed_G1=seed_G2,
seed_G2=seed_G3,
)
pl.subplot(122)
pl.axis("off")
hbar3 = OT_32.sum(axis=0)
pl.title(
r"srGW$(\mathbf{C_3}, \mathbf{h_3},\mathbf{C_2}) =%s$" % (np.round(srgw_32, 3)),
fontsize=fontsize,
)
pos1, pos2 = draw_transp_colored_srGW(
weightedG3,
C3,
weightedG2,
C2,
part_G3,
p1=None,
p2=hbar3,
T=OT_32,
pos1=pos2,
pos2=pos1,
shiftx=3.0,
node_size=node_size,
seed_G1=0,
seed_G2=0,
)
pl.tight_layout()
pl.show()
Add node features
# We add node features with given mean - by clusters
# and inversely proportional to clusters' intra-connectivity
F2 = np.zeros((N2, 1))
for i, c in enumerate(part_G2):
F2[i, 0] = np.random.normal(loc=c, scale=0.01)
F3 = np.zeros((N3, 1))
for i, c in enumerate(part_G3):
F3[i, 0] = np.random.normal(loc=2.0 - c, scale=0.01)
Compute their semi-relaxed Fused Gromov-Wasserstein divergences
alpha = 0.5
# Compute pairwise euclidean distance between node features
M = (F2**2).dot(np.ones((1, N3))) + np.ones((N2, 1)).dot((F3**2).T) - 2 * F2.dot(F3.T)
# 0) FGW_alpha(C2, F2, h2, C3, F3, h3) for reference
OT, log = fused_gromov_wasserstein(
M, C2, C3, h2, h3, symmetric=True, alpha=alpha, log=True
)
fgw = log["fgw_dist"]
# 1) srFGW(C2, F2, h2, C3, F3)
OT_23, log_23 = semirelaxed_fused_gromov_wasserstein(
M, C2, C3, h2, symmetric=True, alpha=0.5, log=True, G0=None
)
srfgw_23 = log_23["srfgw_dist"]
# 2) srFGW(C3, F3, h3, C2, F2)
OT_32, log_32 = semirelaxed_fused_gromov_wasserstein(
M.T, C3, C2, h3, symmetric=None, alpha=alpha, log=True, G0=None
)
srfgw_32 = log_32["srfgw_dist"]
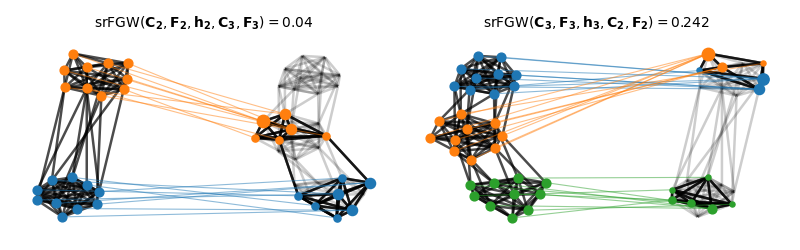
print("FGW(C2, F2, C3, F3) = ", fgw)
print("srGW(C2, F2, h2, C3, F3) = ", srfgw_23)
print("srGW(C3, F3, h3, C2, F2) = ", srfgw_32)
FGW(C2, F2, C3, F3) = 0.3812043286676665
srGW(C2, F2, h2, C3, F3) = 0.025066673141778524
srGW(C3, F3, h3, C2, F2) = 0.2552516366391106
Visualization of the semi-relaxed Fused Gromov-Wasserstein matchings
We color nodes of the graph on the right - then project its node colors based on the optimal transport plan from the srFGW matching NB: colors refer to clusters - not to node features
pl.figure(2, figsize=(8, 2.5))
pl.clf()
pl.subplot(121)
pl.axis("off")
pl.axis
pl.title(
r"srFGW$(\mathbf{C_2},\mathbf{F_2},\mathbf{h_2},\mathbf{C_3},\mathbf{F_3}) =%s$"
% (np.round(srfgw_23, 3)),
fontsize=fontsize,
)
hbar2 = OT_23.sum(axis=0)
pos1, pos2 = draw_transp_colored_srGW(
weightedG2,
C2,
weightedG3,
C3,
part_G2,
p1=None,
p2=hbar2,
T=OT_23,
shiftx=1.5,
node_size=node_size,
seed_G1=seed_G2,
seed_G2=seed_G3,
)
pl.subplot(122)
pl.axis("off")
hbar3 = OT_32.sum(axis=0)
pl.title(
r"srFGW$(\mathbf{C_3}, \mathbf{F_3}, \mathbf{h_3}, \mathbf{C_2}, \mathbf{F_2}) =%s$"
% (np.round(srfgw_32, 3)),
fontsize=fontsize,
)
pos1, pos2 = draw_transp_colored_srGW(
weightedG3,
C3,
weightedG2,
C2,
part_G3,
p1=None,
p2=hbar3,
T=OT_32,
pos1=pos2,
pos2=pos1,
shiftx=3.0,
node_size=node_size,
seed_G1=0,
seed_G2=0,
)
pl.tight_layout()
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.752 seconds)