Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Plot Fused-Gromov-Wasserstein
This example first illustrates the computation of FGW for 1D measures estimated using a Conditional Gradient solver [24].
[24] Vayer Titouan, Chapel Laetitia, Flamary Rémi, Tavenard Romain and Courty Nicolas “Optimal Transport for structured data with application on graphs” International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). 2019.
# Author: Titouan Vayer <titouan.vayer@irisa.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np
import ot
from ot.gromov import gromov_wasserstein, fused_gromov_wasserstein
Generate data
# parameters
# We create two 1D random measures
n = 20 # number of points in the first distribution
n2 = 30 # number of points in the second distribution
sig = 1 # std of first distribution
sig2 = 0.1 # std of second distribution
np.random.seed(0)
phi = np.arange(n)[:, None]
xs = phi + sig * np.random.randn(n, 1)
ys = np.vstack(
(np.ones((n // 2, 1)), 0 * np.ones((n // 2, 1)))
) + sig2 * np.random.randn(n, 1)
phi2 = np.arange(n2)[:, None]
xt = phi2 + sig * np.random.randn(n2, 1)
yt = np.vstack(
(np.ones((n2 // 2, 1)), 0 * np.ones((n2 // 2, 1)))
) + sig2 * np.random.randn(n2, 1)
yt = yt[::-1, :]
p = ot.unif(n)
q = ot.unif(n2)
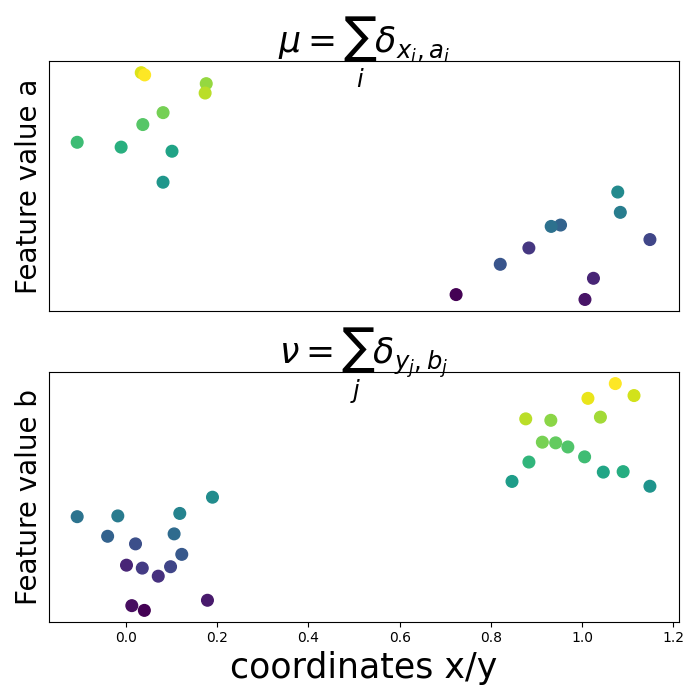
Plot data
# plot the distributions
pl.figure(1, (7, 7))
pl.subplot(2, 1, 1)
pl.scatter(ys, xs, c=phi, s=70)
pl.ylabel("Feature value a", fontsize=20)
pl.title("$\mu=\sum_i \delta_{x_i,a_i}$", fontsize=25, y=1)
pl.xticks(())
pl.yticks(())
pl.subplot(2, 1, 2)
pl.scatter(yt, xt, c=phi2, s=70)
pl.xlabel("coordinates x/y", fontsize=25)
pl.ylabel("Feature value b", fontsize=20)
pl.title("$\\nu=\sum_j \delta_{y_j,b_j}$", fontsize=25, y=1)
pl.yticks(())
pl.tight_layout()
pl.show()
Create structure matrices and across-feature distance matrix
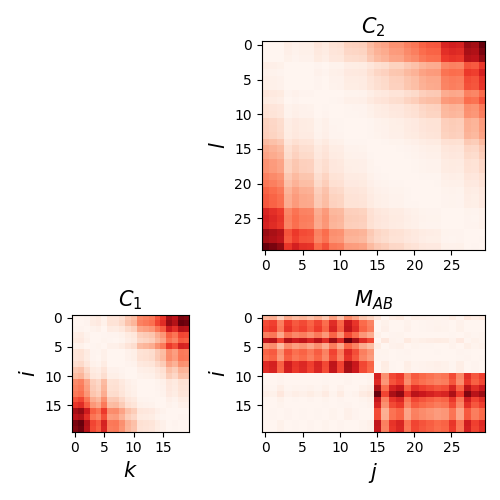
Plot matrices
cmap = "Reds"
pl.figure(2, (5, 5))
fs = 15
l_x = [0, 5, 10, 15]
l_y = [0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
gs = pl.GridSpec(5, 5)
ax1 = pl.subplot(gs[3:, :2])
pl.imshow(C1, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.title("$C_1$", fontsize=fs)
pl.xlabel("$k$", fontsize=fs)
pl.ylabel("$i$", fontsize=fs)
pl.xticks(l_x)
pl.yticks(l_x)
ax2 = pl.subplot(gs[:3, 2:])
pl.imshow(C2, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.title("$C_2$", fontsize=fs)
pl.ylabel("$l$", fontsize=fs)
pl.xticks(())
pl.yticks(l_y)
ax2.set_aspect("auto")
ax3 = pl.subplot(gs[3:, 2:], sharex=ax2, sharey=ax1)
pl.imshow(M, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.yticks(l_x)
pl.xticks(l_y)
pl.ylabel("$i$", fontsize=fs)
pl.title("$M_{AB}$", fontsize=fs)
pl.xlabel("$j$", fontsize=fs)
pl.tight_layout()
ax3.set_aspect("auto")
pl.show()
Compute FGW/GW
It. |Loss |Relative loss|Absolute loss
------------------------------------------------
0|4.734412e+01|0.000000e+00|0.000000e+00
1|2.508254e+01|8.875326e-01|2.226158e+01
2|2.189327e+01|1.456740e-01|3.189279e+00
3|2.189327e+01|1.622743e-16|3.552714e-15
Elapsed time : 0.0017434530000173254 s
It. |Loss |Relative loss|Absolute loss
------------------------------------------------
0|4.683978e+04|0.000000e+00|0.000000e+00
1|3.860061e+04|2.134468e-01|8.239175e+03
2|2.182948e+04|7.682787e-01|1.677113e+04
3|2.182948e+04|0.000000e+00|0.000000e+00
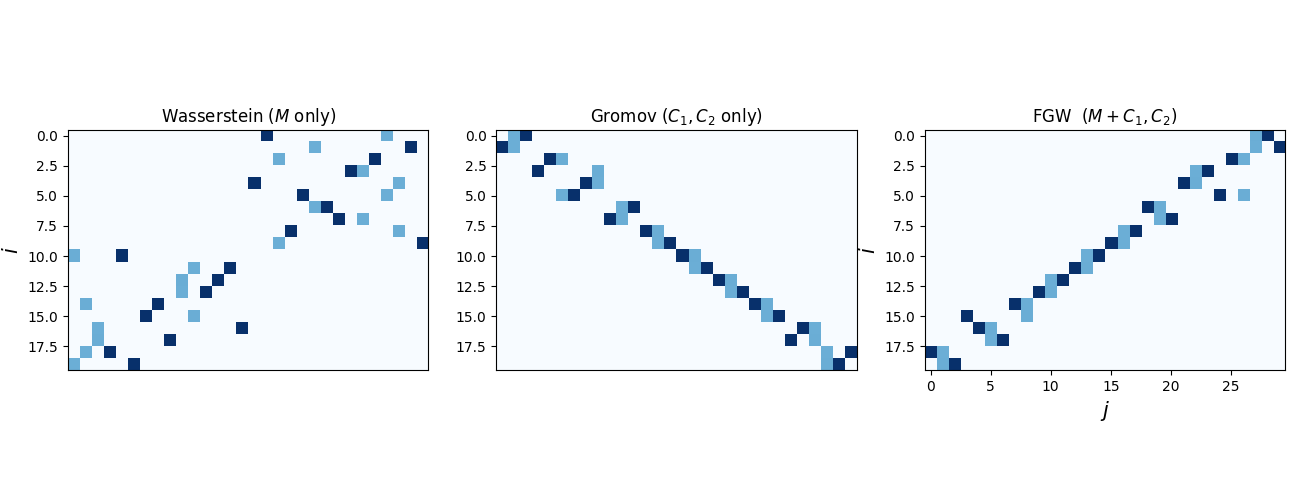
Visualize transport matrices
# visu OT matrix
cmap = "Blues"
fs = 15
pl.figure(3, (13, 5))
pl.clf()
pl.subplot(1, 3, 1)
pl.imshow(Got, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.ylabel("$i$", fontsize=fs)
pl.xticks(())
pl.title("Wasserstein ($M$ only)")
pl.subplot(1, 3, 2)
pl.imshow(Gg, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.title("Gromov ($C_1,C_2$ only)")
pl.xticks(())
pl.subplot(1, 3, 3)
pl.imshow(Gwg, cmap=cmap, interpolation="nearest")
pl.title("FGW ($M+C_1,C_2$)")
pl.xlabel("$j$", fontsize=fs)
pl.ylabel("$i$", fontsize=fs)
pl.tight_layout()
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.675 seconds)