Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Gaussian Mixture Model OT Barycenters
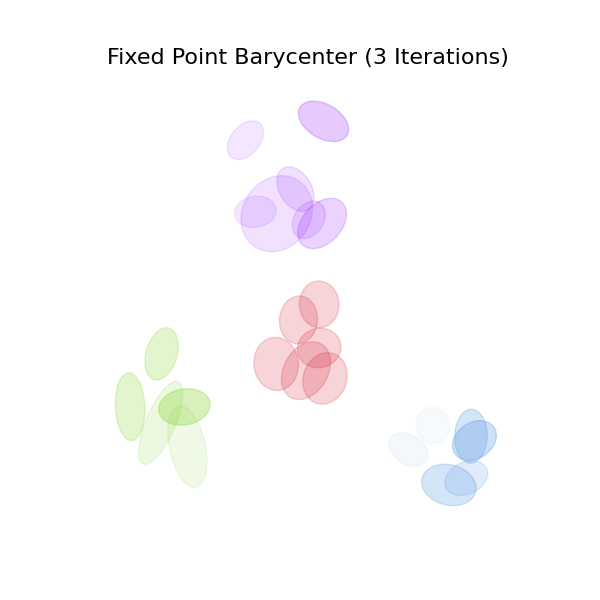
This example illustrates the computation of a barycenter between Gaussian Mixtures in the sense of GMM-OT [69]. This computation is done using the fixed-point method for OT barycenters with generic costs [77], for which POT provides a general solver, and a specific GMM solver. Note that this is a ‘free-support’ method, implying that the number of components of the barycenter GMM and their weights are fixed.
The idea behind GMM-OT barycenters is to see the GMMs as discrete measures over the space of Gaussian distributions \(\mathcal{N}\) (or equivalently the Bures-Wasserstein manifold), and to compute barycenters with respect to the 2-Wasserstein distance between measures in \(\mathcal{P}(\mathcal{N})\): a gaussian mixture is a finite combination of Diracs on specific gaussians, and two mixtures are compared with the 2-Wasserstein distance on this space, where ground cost the squared Bures distance between gaussians.
[69] Delon, J., & Desolneux, A. (2020). A Wasserstein-type distance in the space of Gaussian mixture models. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 13(2), 936-970.
[77] Tanguy, Eloi and Delon, Julie and Gozlan, Nathaël (2024). Computing Barycentres of Measures for Generic Transport Costs. arXiv preprint 2501.04016 (2024)
# Author: Eloi Tanguy <eloi.tanguy@math.cnrs.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
Generate data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
import ot
from ot.gmm import gmm_barycenter_fixed_point
K = 3 # number of GMMs
d = 2 # dimension
n = 6 # number of components of the desired barycenter
def get_random_gmm(K, d, seed=0, min_cov_eig=1, cov_scale=1e-2):
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=seed)
means = rng.randn(K, d)
P = rng.randn(K, d, d) * cov_scale
# C[k] = P[k] @ P[k]^T + min_cov_eig * I
covariances = np.einsum("kab,kcb->kac", P, P)
covariances += min_cov_eig * np.array([np.eye(d) for _ in range(K)])
weights = rng.random(K)
weights /= np.sum(weights)
return means, covariances, weights
m_list = [5, 6, 7] # number of components in each GMM
offsets = [np.array([-3, 0]), np.array([2, 0]), np.array([0, 4])]
means_list = [] # list of means for each GMM
covs_list = [] # list of covariances for each GMM
w_list = [] # list of weights for each GMM
# generate GMMs
for k in range(K):
means, covs, b = get_random_gmm(
m_list[k], d, seed=k, min_cov_eig=0.25, cov_scale=0.5
)
means = means / 2 + offsets[k][None, :]
means_list.append(means)
covs_list.append(covs)
w_list.append(b)
Compute the barycenter using the fixed-point method
init_means, init_covs, _ = get_random_gmm(n, d, seed=0)
weights = ot.unif(K) # barycenter coefficients
means_bar, covs_bar, log = gmm_barycenter_fixed_point(
means_list,
covs_list,
w_list,
init_means,
init_covs,
weights,
iterations=3,
log=True,
)
Define plotting functions
# draw a covariance ellipse
def draw_cov(mu, C, color=None, label=None, nstd=1, alpha=0.5, ax=None):
def eigsorted(cov):
vals, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(cov)
order = vals.argsort()[::-1].copy()
return vals[order], vecs[:, order]
vals, vecs = eigsorted(C)
theta = np.degrees(np.arctan2(*vecs[:, 0][::-1]))
w, h = 2 * nstd * np.sqrt(vals)
ell = Ellipse(
xy=(mu[0], mu[1]),
width=w,
height=h,
alpha=alpha,
angle=theta,
facecolor=color,
edgecolor=color,
label=label,
fill=True,
)
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
ax.add_artist(ell)
# draw a gmm as a set of ellipses with weights shown in alpha value
def draw_gmm(ms, Cs, ws, color=None, nstd=0.5, alpha=1, label=None, ax=None):
for k in range(ms.shape[0]):
draw_cov(
ms[k], Cs[k], color, label if k == 0 else None, nstd, alpha * ws[k], ax=ax
)
Plot the results
c_list = ["#7ED321", "#4A90E2", "#9013FE", "#F5A623"]
c_bar = "#D0021B"
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
axis = [-4, 4, -2, 6]
ax.set_title("Fixed Point Barycenter (3 Iterations)", fontsize=16)
for k in range(K):
draw_gmm(means_list[k], covs_list[k], w_list[k], color=c_list[k], ax=ax)
draw_gmm(means_bar, covs_bar, ot.unif(n), color=c_bar, ax=ax)
ax.axis(axis)
ax.axis("off")
(np.float64(-4.0), np.float64(4.0), np.float64(-2.0), np.float64(6.0))
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.095 seconds)