Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Optimal Transport solvers comparison
This example illustrates the solutions returns for different variants of exact, regularized and unbalanced OT solvers.
# Author: Remi Flamary <remi.flamary@unice.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as pl
import ot
import ot.plot
from ot.datasets import make_1D_gauss as gauss
Generate data
Plot distributions and loss matrix
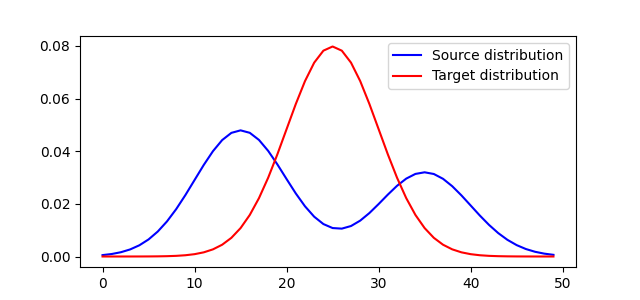
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f95b56e82e0>
pl.figure(2, figsize=(5, 5))
ot.plot.plot1D_mat(a, b, M, "Cost matrix M")
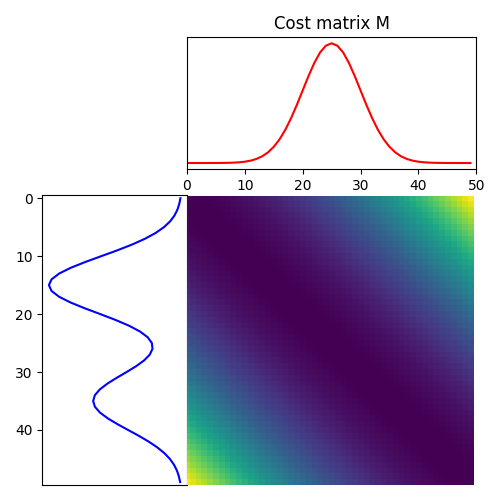
(<Axes: >, <Axes: >, <Axes: >)
Define Group lasso regularization and gradient
The groups are the first and second half of the columns of G
def reg_gl(G): # group lasso + small l2 reg
G1 = G[: n // 2, :] ** 2
G2 = G[n // 2 :, :] ** 2
gl1 = np.sum(np.sqrt(np.sum(G1, 0)))
gl2 = np.sum(np.sqrt(np.sum(G2, 0)))
return gl1 + gl2 + 0.1 * np.sum(G**2)
def grad_gl(G): # gradient of group lasso + small l2 reg
G1 = G[: n // 2, :]
G2 = G[n // 2 :, :]
gl1 = G1 / np.sqrt(np.sum(G1**2, 0, keepdims=True) + 1e-8)
gl2 = G2 / np.sqrt(np.sum(G2**2, 0, keepdims=True) + 1e-8)
return np.concatenate((gl1, gl2), axis=0) + 0.2 * G
reg_type_gl = (reg_gl, grad_gl)
Set up parameters for solvers and solve
lst_regs = ["No Reg.", "Entropic", "L2", "Group Lasso + L2"]
lst_unbalanced = [
"Balanced",
"Unbalanced KL",
"Unbalanced L2",
"Unb. TV (Partial)",
] # ["Balanced", "Unb. KL", "Unb. L2", "Unb L1 (partial)"]
lst_solvers = [ # name, param for ot.solve function
# balanced OT
("Exact OT", dict()),
("Entropic Reg. OT", dict(reg=0.005)),
("L2 Reg OT", dict(reg=1, reg_type="l2")),
("Group Lasso Reg. OT", dict(reg=0.1, reg_type=reg_type_gl)),
# unbalanced OT KL
("Unbalanced KL No Reg.", dict(unbalanced=0.005)),
(
"Unbalanced KL with KL Reg.",
dict(reg=0.0005, unbalanced=0.005, unbalanced_type="kl", reg_type="kl"),
),
(
"Unbalanced KL with L2 Reg.",
dict(reg=0.5, reg_type="l2", unbalanced=0.005, unbalanced_type="kl"),
),
(
"Unbalanced KL with Group Lasso Reg.",
dict(reg=0.1, reg_type=reg_type_gl, unbalanced=0.05, unbalanced_type="kl"),
),
# unbalanced OT L2
("Unbalanced L2 No Reg.", dict(unbalanced=0.5, unbalanced_type="l2")),
(
"Unbalanced L2 with KL Reg.",
dict(reg=0.001, unbalanced=0.2, unbalanced_type="l2"),
),
(
"Unbalanced L2 with L2 Reg.",
dict(reg=0.1, reg_type="l2", unbalanced=0.2, unbalanced_type="l2"),
),
(
"Unbalanced L2 with Group Lasso Reg.",
dict(reg=0.05, reg_type=reg_type_gl, unbalanced=0.7, unbalanced_type="l2"),
),
# unbalanced OT TV
("Unbalanced TV No Reg.", dict(unbalanced=0.1, unbalanced_type="tv")),
(
"Unbalanced TV with KL Reg.",
dict(reg=0.001, unbalanced=0.01, unbalanced_type="tv"),
),
(
"Unbalanced TV with L2 Reg.",
dict(reg=0.1, reg_type="l2", unbalanced=0.01, unbalanced_type="tv"),
),
(
"Unbalanced TV with Group Lasso Reg.",
dict(reg=0.02, reg_type=reg_type_gl, unbalanced=0.01, unbalanced_type="tv"),
),
]
lst_plans = []
for name, param in lst_solvers:
G = ot.solve(M, a, b, **param).plan
lst_plans.append(G)
Plot plans
pl.figure(3, figsize=(9, 9))
for i, bname in enumerate(lst_unbalanced):
for j, rname in enumerate(lst_regs):
pl.subplot(len(lst_unbalanced), len(lst_regs), i * len(lst_regs) + j + 1)
plan = lst_plans[i * len(lst_regs) + j]
m2 = plan.sum(0)
m1 = plan.sum(1)
m1, m2 = m1 / a.max(), m2 / b.max()
pl.imshow(plan, cmap="Greys")
pl.plot(x, m2 * 10, "r")
pl.plot(m1 * 10, x, "b")
pl.plot(x, b / b.max() * 10, "r", alpha=0.3)
pl.plot(a / a.max() * 10, x, "b", alpha=0.3)
# pl.axis('off')
pl.tick_params(
left=False, right=False, labelleft=False, labelbottom=False, bottom=False
)
if i == 0:
pl.title(rname)
if j == 0:
pl.ylabel(bname, fontsize=14)
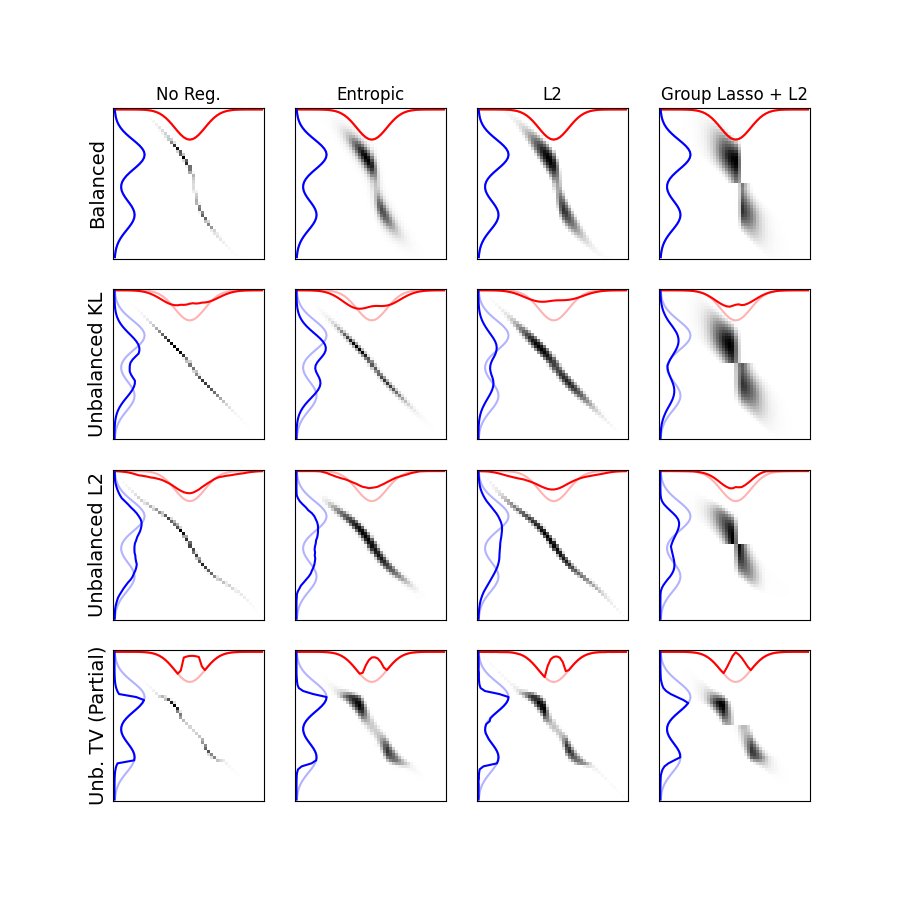
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.673 seconds)