Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Linear OT mapping estimation
Note
Example updated in release: 0.9.1.
# Author: Remi Flamary <remi.flamary@unice.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
import os
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import ot
Generate data
n = 1000
d = 2
sigma = 0.1
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
# source samples
angles = rng.rand(n, 1) * 2 * np.pi
xs = np.concatenate((np.sin(angles), np.cos(angles)), axis=1) + sigma * rng.randn(n, 2)
xs[: n // 2, 1] += 2
# target samples
anglet = rng.rand(n, 1) * 2 * np.pi
xt = np.concatenate((np.sin(anglet), np.cos(anglet)), axis=1) + sigma * rng.randn(n, 2)
xt[: n // 2, 1] += 2
A = np.array([[1.5, 0.7], [0.7, 1.5]])
b = np.array([[4, 2]])
xt = xt.dot(A) + b
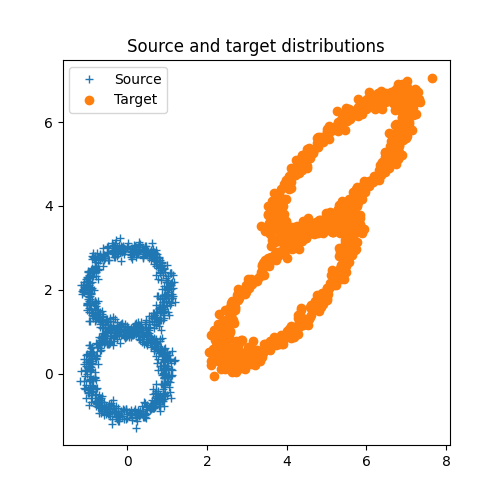
Plot data
plt.figure(1, (5, 5))
plt.plot(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], "+")
plt.plot(xt[:, 0], xt[:, 1], "o")
plt.legend(("Source", "Target"))
plt.title("Source and target distributions")
plt.show()
Estimate linear mapping and transport
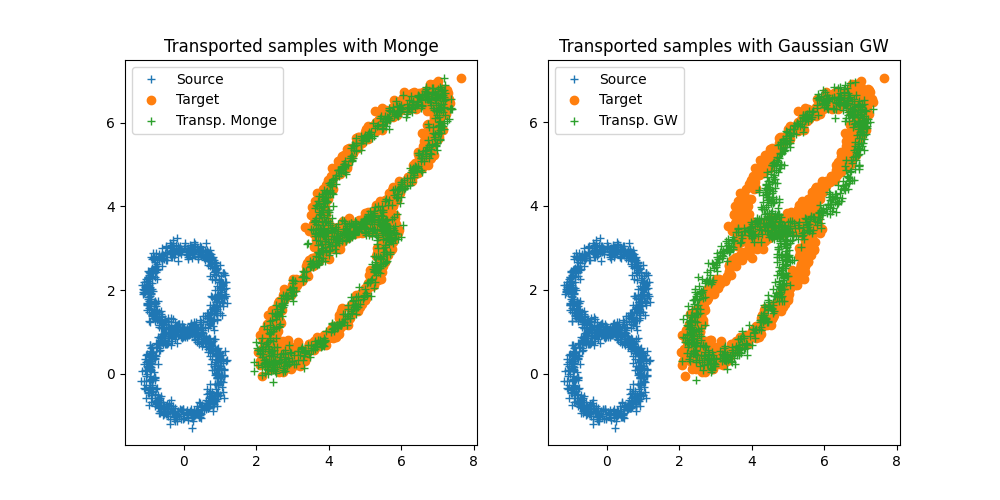
Plot transported samples
plt.figure(2, (10, 5))
plt.clf()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], "+")
plt.plot(xt[:, 0], xt[:, 1], "o")
plt.plot(xst[:, 0], xst[:, 1], "+")
plt.legend(("Source", "Target", "Transp. Monge"), loc=0)
plt.title("Transported samples with Monge")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], "+")
plt.plot(xt[:, 0], xt[:, 1], "o")
plt.plot(xstgw[:, 0], xstgw[:, 1], "+")
plt.legend(("Source", "Target", "Transp. GW"), loc=0)
plt.title("Transported samples with Gaussian GW")
plt.show()
Load image data
def im2mat(img):
"""Converts and image to matrix (one pixel per line)"""
return img.reshape((img.shape[0] * img.shape[1], img.shape[2]))
def mat2im(X, shape):
"""Converts back a matrix to an image"""
return X.reshape(shape)
def minmax(img):
return np.clip(img, 0, 1)
# Loading images
this_file = os.path.realpath("__file__")
data_path = os.path.join(Path(this_file).parent.parent.parent, "data")
I1 = plt.imread(os.path.join(data_path, "ocean_day.jpg")).astype(np.float64) / 256
I2 = plt.imread(os.path.join(data_path, "ocean_sunset.jpg")).astype(np.float64) / 256
X1 = im2mat(I1)
X2 = im2mat(I2)
Estimate mapping and adapt
# Monge mapping
mapping = ot.da.LinearTransport()
mapping.fit(Xs=X1, Xt=X2)
xst = mapping.transform(Xs=X1)
xts = mapping.inverse_transform(Xt=X2)
I1t = minmax(mat2im(xst, I1.shape))
I2t = minmax(mat2im(xts, I2.shape))
# gaussian GW mapping
mapping = ot.da.LinearGWTransport()
mapping.fit(Xs=X1, Xt=X2)
xstgw = mapping.transform(Xs=X1)
xtsgw = mapping.inverse_transform(Xt=X2)
I1tgw = minmax(mat2im(xstgw, I1.shape))
I2tgw = minmax(mat2im(xtsgw, I2.shape))
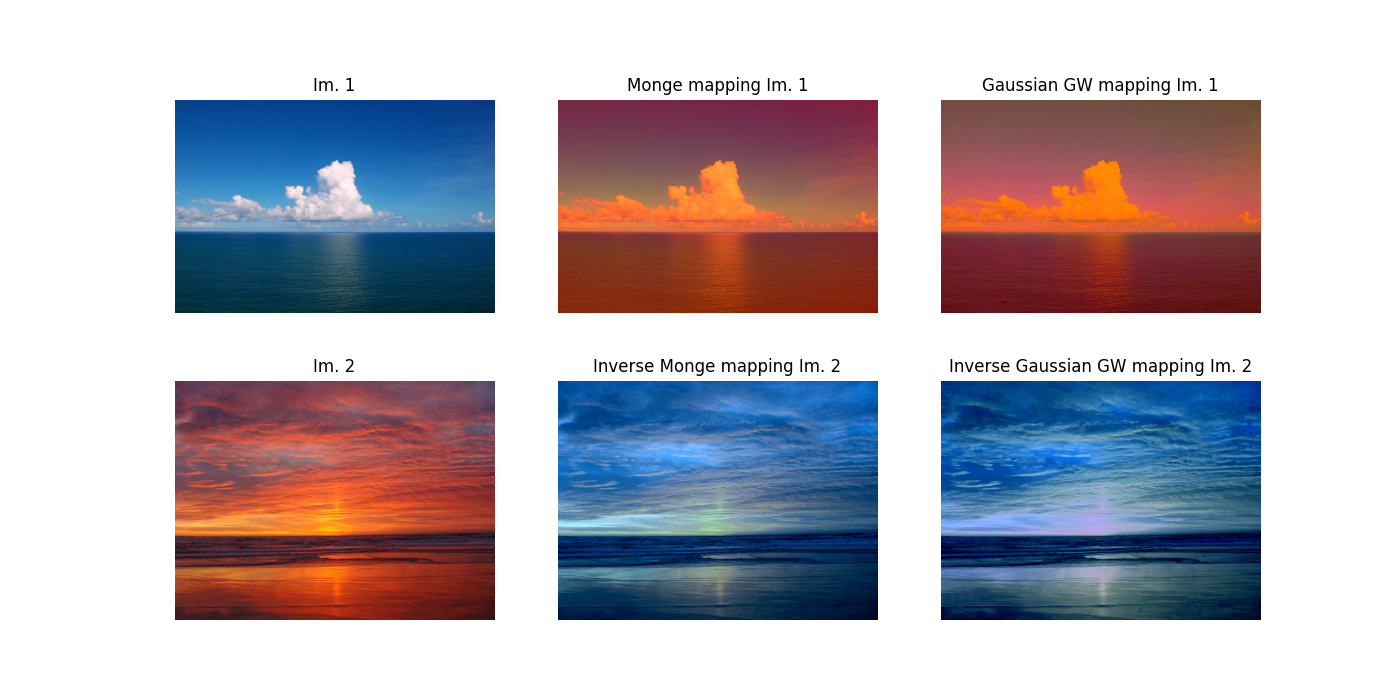
Plot transformed images
plt.figure(3, figsize=(14, 7))
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(I1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Im. 1")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.imshow(I2)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Im. 2")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(I1t)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Monge mapping Im. 1")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.imshow(I2t)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Inverse Monge mapping Im. 2")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(I1tgw)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Gaussian GW mapping Im. 1")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.imshow(I2tgw)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Inverse Gaussian GW mapping Im. 2")

Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Inverse Gaussian GW mapping Im. 2')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.372 seconds)