Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
2D examples of exact and entropic unbalanced optimal transport
Note
Example added in release: 0.8.2.
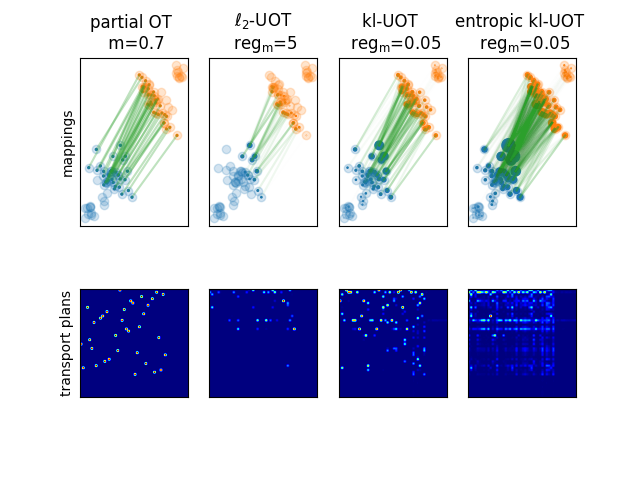
This example is designed to show how to compute unbalanced and partial OT in POT.
UOT aims at solving the following optimization problem:
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}W = \min_{\gamma} <\gamma, \mathbf{M}>_F + \mathrm{reg}\cdot\Omega(\gamma) + \mathrm{reg_m} \cdot \mathrm{div}(\gamma \mathbf{1}, \mathbf{a}) + \mathrm{reg_m} \cdot \mathrm{div}(\gamma^T \mathbf{1}, \mathbf{b})\\s.t. \gamma \geq 0\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
where \(\mathrm{div}\) is a divergence. When using the entropic UOT, \(\mathrm{reg}>0\) and \(\mathrm{div}\) should be the Kullback-Leibler divergence. When solving exact UOT, \(\mathrm{reg}=0\) and \(\mathrm{div}\) can be either the Kullback-Leibler or the quadratic divergence. Using \(\ell_1\) norm gives the so-called partial OT.
# Author: Laetitia Chapel <laetitia.chapel@univ-ubs.fr>
# License: MIT License
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as pl
import ot
Generate data
n = 40 # nb samples
mu_s = np.array([-1, -1])
cov_s = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]])
mu_t = np.array([4, 4])
cov_t = np.array([[1, -0.8], [-0.8, 1]])
np.random.seed(0)
xs = ot.datasets.make_2D_samples_gauss(n, mu_s, cov_s)
xt = ot.datasets.make_2D_samples_gauss(n, mu_t, cov_t)
n_noise = 10
xs = np.concatenate((xs, (np.random.rand(n_noise, 2) - 4)), axis=0)
xt = np.concatenate((xt, (np.random.rand(n_noise, 2) + 6)), axis=0)
n = n + n_noise
a, b = np.ones((n,)) / n, np.ones((n,)) / n # uniform distribution on samples
# loss matrix
M = ot.dist(xs, xt)
M /= M.max()
Compute entropic kl-regularized UOT, kl- and l2-regularized UOT
reg = 0.005
reg_m_kl = 0.05
reg_m_l2 = 5
mass = 0.7
entropic_kl_uot = ot.unbalanced.sinkhorn_unbalanced(a, b, M, reg, reg_m_kl)
kl_uot = ot.unbalanced.mm_unbalanced(a, b, M, reg_m_kl, div="kl")
l2_uot = ot.unbalanced.mm_unbalanced(a, b, M, reg_m_l2, div="l2")
partial_ot = ot.partial.partial_wasserstein(a, b, M, m=mass)
Plot the results
pl.figure(2)
transp = [partial_ot, l2_uot, kl_uot, entropic_kl_uot]
title = [
"partial OT \n m=" + str(mass),
"$\ell_2$-UOT \n $\mathrm{reg_m}$=" + str(reg_m_l2),
"kl-UOT \n $\mathrm{reg_m}$=" + str(reg_m_kl),
"entropic kl-UOT \n $\mathrm{reg_m}$=" + str(reg_m_kl),
]
for p in range(4):
pl.subplot(2, 4, p + 1)
P = transp[p]
if P.sum() > 0:
P = P / P.max()
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if P[i, j] > 0:
pl.plot(
[xs[i, 0], xt[j, 0]],
[xs[i, 1], xt[j, 1]],
color="C2",
alpha=P[i, j] * 0.3,
)
pl.scatter(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], c="C0", alpha=0.2)
pl.scatter(xt[:, 0], xt[:, 1], c="C1", alpha=0.2)
pl.scatter(xs[:, 0], xs[:, 1], c="C0", s=P.sum(1).ravel() * (1 + p) * 2)
pl.scatter(xt[:, 0], xt[:, 1], c="C1", s=P.sum(0).ravel() * (1 + p) * 2)
pl.title(title[p])
pl.yticks(())
pl.xticks(())
if p < 1:
pl.ylabel("mappings")
pl.subplot(2, 4, p + 5)
pl.imshow(P, cmap="jet")
pl.yticks(())
pl.xticks(())
if p < 1:
pl.ylabel("transport plans")
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.076 seconds)