Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Nyström approximation for OT
Shows how to use Nyström kernel approximation for approximating the Sinkhorn algorithm in linear time.
# Author: Titouan Vayer <titouan.vayer@inria.fr>
#
# License: MIT License
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
import numpy as np
from ot.lowrank import kernel_nystroem, sinkhorn_low_rank_kernel
from ot.bregman import empirical_sinkhorn_nystroem
import math
import ot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
Generate data
offset = 1
n_samples_per_blob = 500 # We use 2D ''blobs'' data
random_state = 42
std = 0.2 # standard deviation
np.random.seed(random_state)
centers = np.array(
[
[-offset, -offset], # Class 0 - blob 1
[-offset, offset], # Class 0 - blob 2
[offset, -offset], # Class 1 - blob 1
[offset, offset], # Class 1 - blob 2
]
)
X_list = []
y_list = []
for i, center in enumerate(centers):
blob_points = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_blob, 2) * std + center
label = 0 if i < 2 else 1
X_list.append(blob_points)
y_list.append(np.full(n_samples_per_blob, label))
X = np.vstack(X_list)
y = np.concatenate(y_list)
Xs = X[y == 0] # source data
Xt = X[y == 1] # target data
Plot data
plt.scatter(Xs[:, 0], Xs[:, 1], label="Source")
plt.scatter(Xt[:, 0], Xt[:, 1], label="Target")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7ff8a942afe0>
Compute the Nyström approximation of the Gaussian kernel
reg = 5.0 # proportional to the std of the Gaussian kernel
anchors = 10 # number of anchor points for the Nyström approximation
ot.tic()
left_factor, right_factor = kernel_nystroem(
Xs, Xt, anchors=anchors, sigma=math.sqrt(reg / 2.0), random_state=random_state
)
ot.toc()
Elapsed time : 0.0008147499993356178 s
0.0008147499993356178
Use this approximation in a Sinkhorn algorithm with low rank kernel. Each matrix/vector product in the Sinkhorn is accelerated since \(Kv = K_1 (K_2^\top v)\) can be computed in \(O(nr)\) time instead of \(O(n^2)\)
numItermax = 1000
stopThr = 1e-7
verbose = True
a, b = None, None
warn = True
warmstart = None
ot.tic()
u, v, dict_log = sinkhorn_low_rank_kernel(
K1=left_factor,
K2=right_factor,
a=a,
b=b,
numItermax=numItermax,
stopThr=stopThr,
verbose=verbose,
log=True,
warn=warn,
warmstart=warmstart,
)
ot.toc()
It. |Err
-------------------
0|7.482235e-05|
Elapsed time : 0.000984148000497953 s
0.000984148000497953
Compare with Sinkhorn
It. |Err
-------------------
0|7.517180e-05|
Elapsed time : 0.013083940999422339 s
0.013083940999422339
Use directly ot.bregman.empirical_sinkhorn_nystroem
ot.tic()
G_nys = empirical_sinkhorn_nystroem(
Xs,
Xt,
anchors=anchors,
reg=reg,
numItermax=numItermax,
verbose=True,
random_state=random_state,
)[:]
ot.toc()
It. |Err
-------------------
0|7.482235e-05|
Elapsed time : 0.0033734499993443023 s
0.0033734499993443023
ot.tic()
G_sinkh = ot.bregman.empirical_sinkhorn(
Xs, Xt, reg=reg, numIterMax=numItermax, verbose=True
)
ot.toc()
It. |Err
-------------------
0|7.517180e-05|
Elapsed time : 0.016696963999493164 s
0.016696963999493164
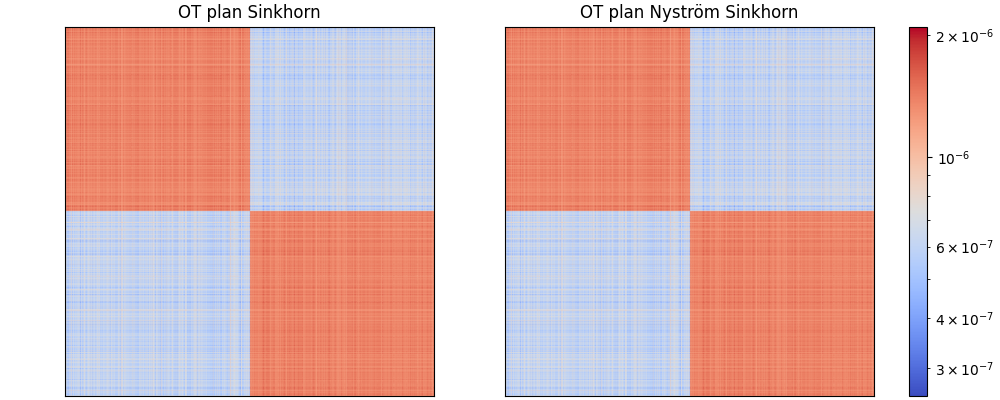
Compare OT plans
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4), constrained_layout=True)
vmin = min(G_sinkh.min(), G_nys.min())
vmax = max(G_sinkh.max(), G_nys.max())
norm = LogNorm(vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
im0 = ax[0].imshow(G_sinkh, norm=norm, cmap="coolwarm")
im1 = ax[1].imshow(G_nys, norm=norm, cmap="coolwarm")
cbar = fig.colorbar(im1, ax=ax, orientation="vertical", fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
ax[0].set_title("OT plan Sinkhorn")
ax[1].set_title("OT plan Nyström Sinkhorn")
for a in ax:
a.set_xticks([])
a.set_yticks([])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.055 seconds)